“It takes a lot of effort to make a building look effortless” – Norman Foster.
3D printing is now transforming that effort, streamlining the design and construction process like never before.

3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, started in the early 1980s. The first patent for the technology was filed by Charles Hull in 1986, who invented stereolithography (SLA). Hull’s innovation allowed people to turn digital designs into physical objects by layering material, almost like a futuristic version of a building with LEGO bricks but guided by a computer.
.webp)
Imagine being able to create something complex and detailed, not by carving or molding, but by building it layer by layer from the ground up. 3D printing makes this possible, using materials like plastic, metal, or even concrete to bring digital designs to life. This technology is revolutionary because it enables people to produce customized, intricate, and even one-of-a-kind products, often faster and cheaper than traditional manufacturing.
.webp)
One of the most powerful examples of 3D printing’s impact is the construction of the world’s first 3D-printed house by DUS Architects in the Netherlands. Using recycled materials, they printed an entire house, showing the world that sustainable, affordable housing could be built quickly and with minimal waste. This project wasn’t just a technological feat, it was a beacon of hope for people in need of shelter, offering a glimpse of a future where housing might be more accessible to everyone.
.webp)
.webp)
By the early 2010s, many architecture and design firms had begun to widely adopt 3D printing technology, recognizing its potential to transform the industry. It became an essential tool for creating detailed models, testing complex design concepts, and even fabricating full-scale building components. The ability to quickly iterate an experiment with designs accelerated innovation and pushed the boundaries of what architects and designers could achieve.
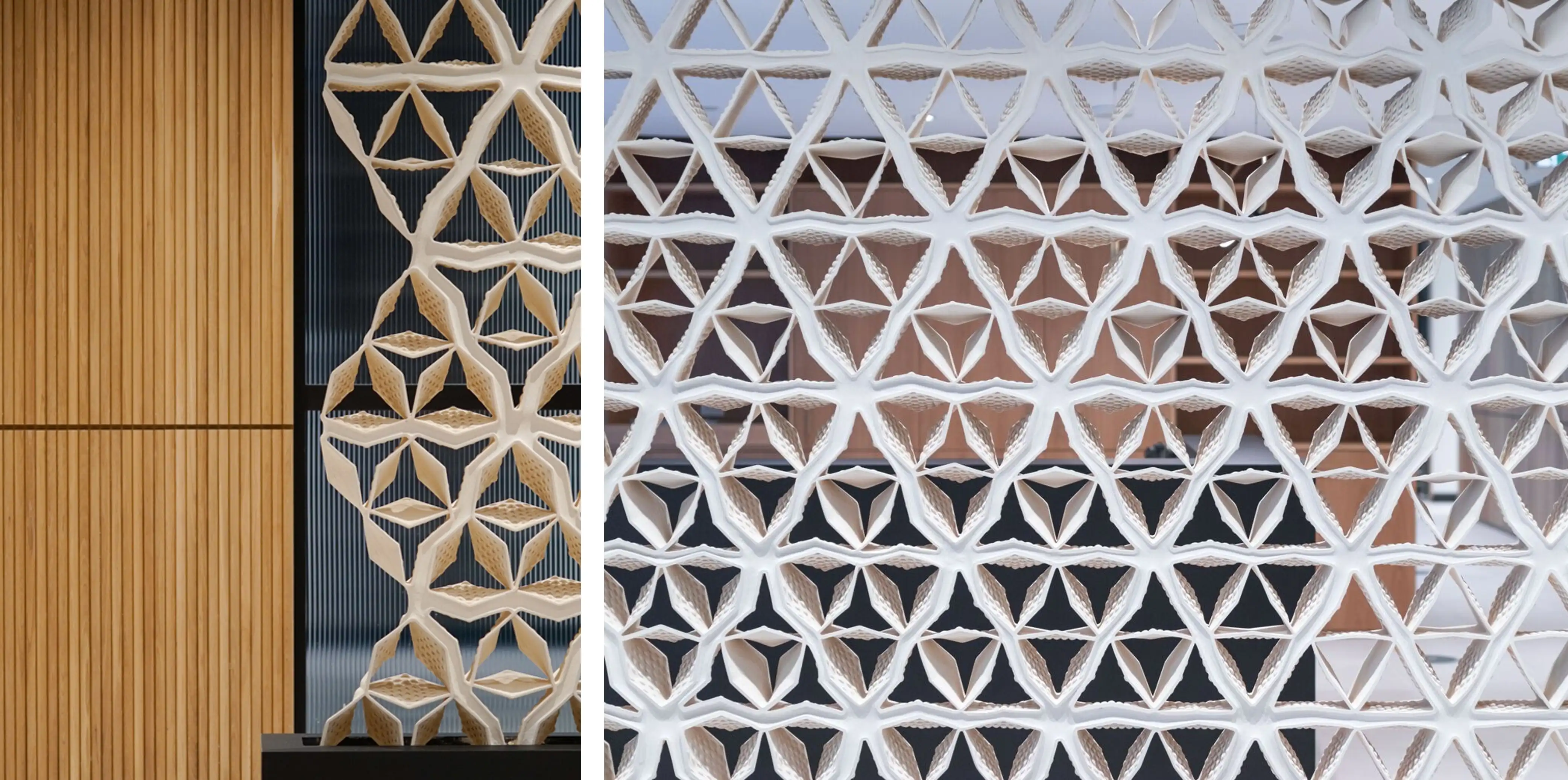
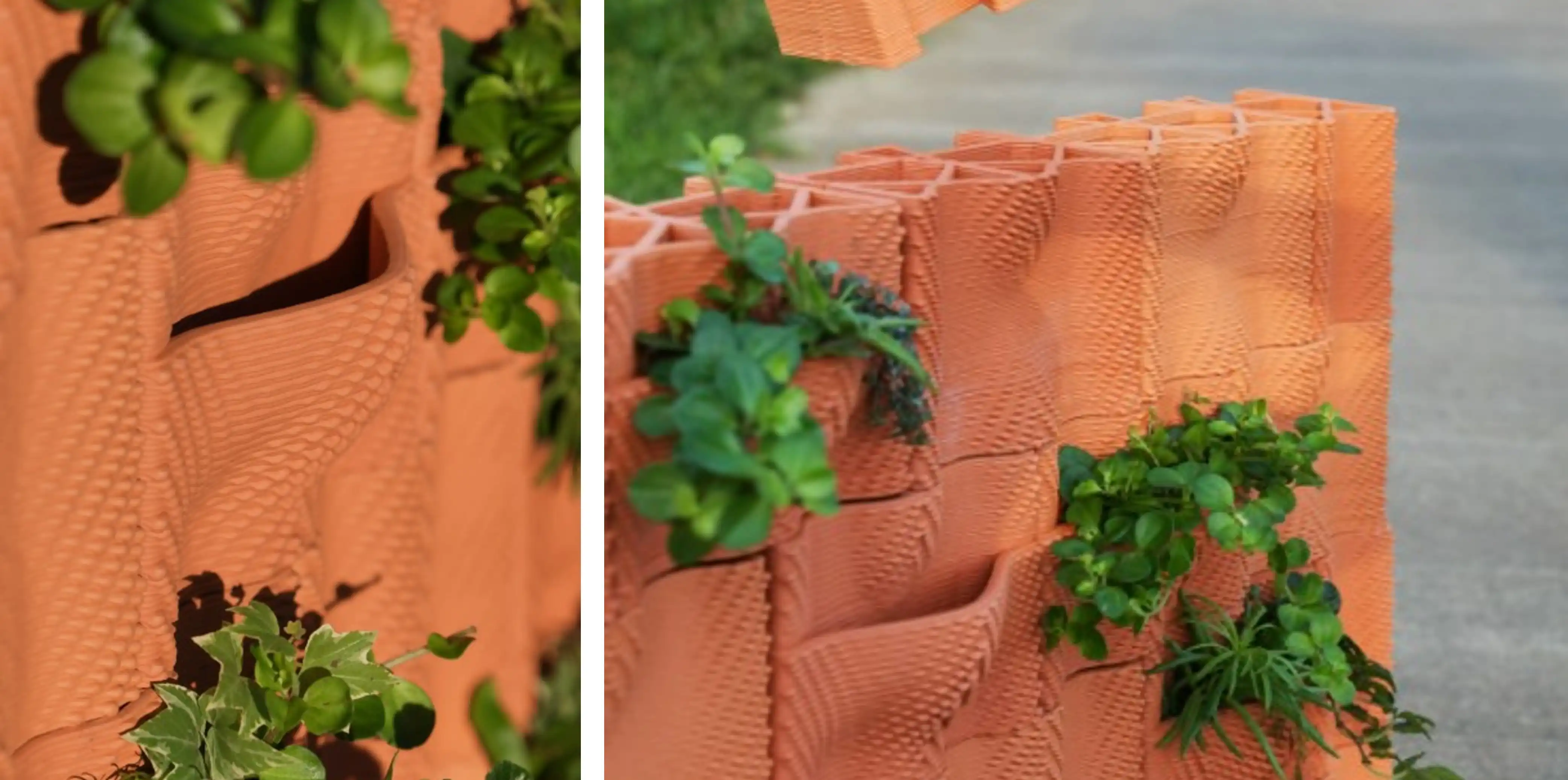
Inspired by breakthroughs like the 3D-printed house, architects and designers have started using 3D printing to create wall panels with intricate patterns, dynamic textures, and even built-in functionalities like insulation or ventilation.
The field of architectural design has changed significantly in recent years due to technological advancements and the most advanced innovation in the construction industry is 3D Printing. Out of all the emerging possibilities of 3D printing, 3D printed wall panels have emerged as a revolutionary solution, providing new perspectives for both aesthetic and functional design. The 3D printed panels are often lighter, stronger, and customizable as compared to the traditionally built counterparts.
The intricate designs, which were once impossible, 3d printing builds the structures layer by layer, unlike the traditional fabrication techniques. Creative boundaries can be pushed without compromising structural integrity exploring fluid, organic curves to sharp and geometrical patterns. For example, Zaha Hadid Architects reduced 25% material waste by utilizing 3D printing while creating a façade.

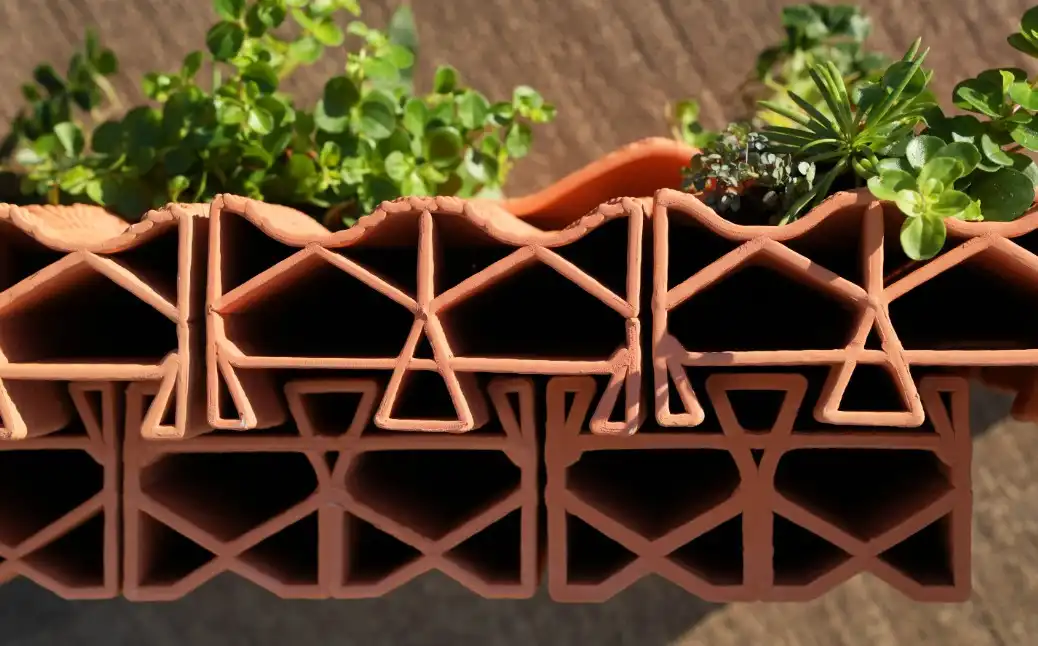
The materials used in 3D printed wall panels differ greatly, including bioplastics, concrete, and composite materials which are suitable for a range of applications. To enhance the functionality of the 3D-printed wall panels, various smart materials such as sound-absorbing or heat-resistant elements are incorporated. Additionally, in modern building,s it contributes to both aesthetic and practical improvements considering form and function by allowing the seamless integration of lighting, ventilation, and insulation.

Around 30% to 40% of global waste was generated by the construction industry in the year 2022. By utilizing 3D printing, it reduces waste drastically by only using the materials required. Large-scale printers can accelerate the construction timelines, lowering costs while creating the entire building sections. This method is particularly useful for addressing housing shortages and constructing emergency shelters in disaster-stricken areas. Today, 3D printed architecture is a viable mainstream solution with robotic arms and multi-axis printers enabling rapid and high-precision fabrication.

3D-printed wall panels are transforming how we design and build both interior and exterior spaces. Here’s a breakdown of the process:

Architects and Designers must learn and understand both the design principles and fabrication techniques. 3D-Printed Wall Panels Workshop at PAACADEMY now offers hands-on experience which will cover all aspects of algorithmic design in Grasshopper to generating custom G-code for precise printer control.
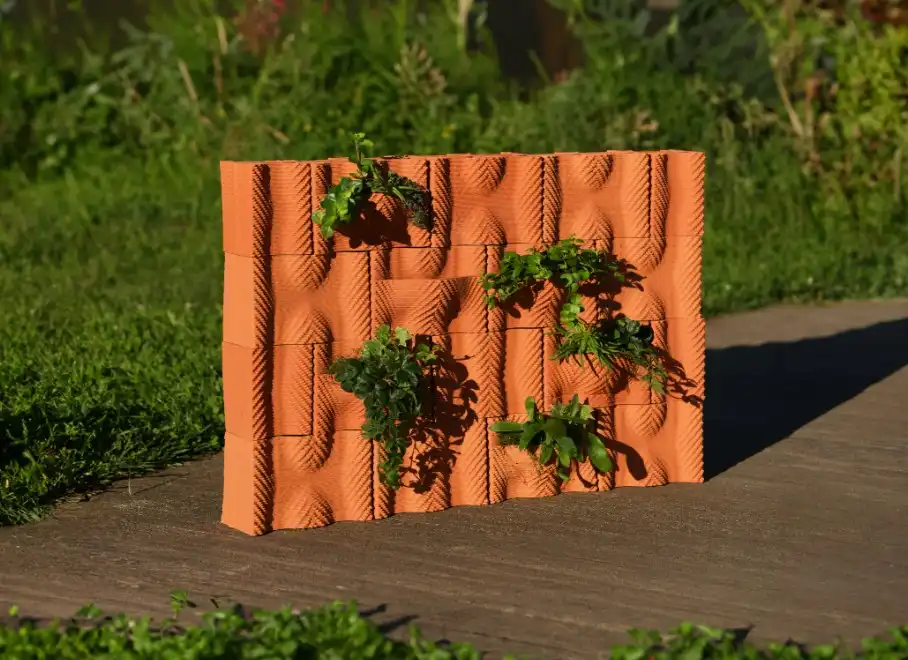

3D-printed wall panels represent a symbol of potential as urbanization accelerates and sustainability becomes predominant. They allow designers to reimagine the spaces we inhabit, and build faster, smarter, and more sustainable worldwide. Whether crafting a sculptural art installation or constructing affordable housing, mastering 3D printing opens doors to endless creative opportunities.
With the ability to create lightweight, durable, and customizable designs, this technology allows professionals to push the boundaries of creativity while optimizing resources. Whether for residential, commercial, or artistic applications, mastering 3D printing techniques can lead to groundbreaking design solutions.
You must be logged in to comment.