
It is not always easy to find the best software for your design needs. Autodesk Revit and Rhino 3D are often compared, but they should actually be seen as complementary tools rather than adversaries. To make a long story short, architects and builders typically lean towards Revit for its strengths in BIM workflows, while industrial designers and 3D artists prefer Rhino for its NURBS-based precision and modeling flexibility. In a way, Rhino translates your creative visions accurately, while Revit helps make them a tangible reality.
This guide offers a comprehensive comparison between the two software tools to help you make an informed decision on how best to use them together or individually.
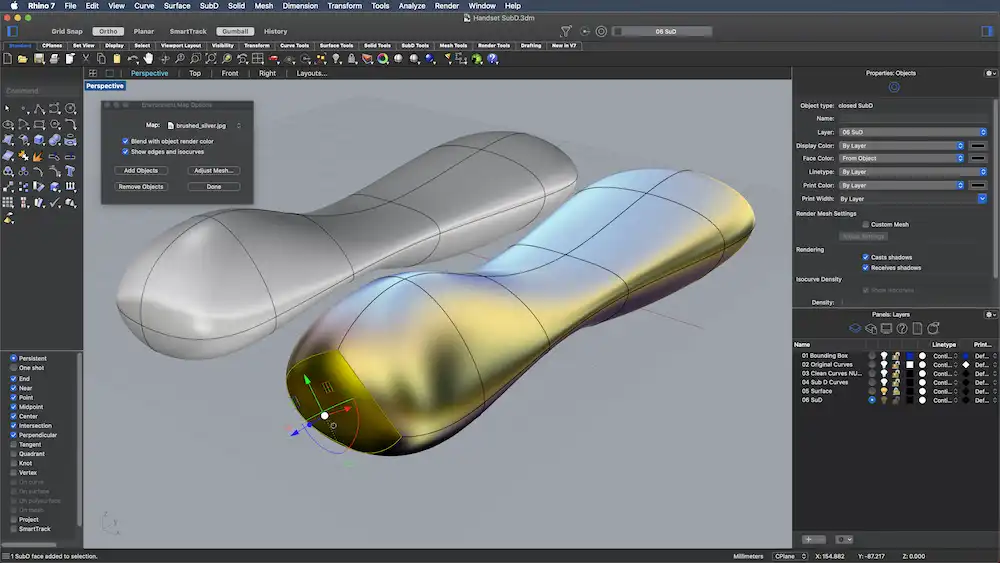
Rhino 3D, short for Rhinoceros 3D, was developed by Robert McNeel & Associates in 1998. It is a 3D modeling software used in various applications such as computer-aided design (CAD), computer-aided manufacturing (CAM), rapid prototyping, 3D printing, reverse engineering, and computational design capabilities through its visual programming platform, Grasshopper3D.
Rhino uses NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) geometry to produce precise surface models, which is essential across industries including architecture, industrial design (e.g., automotive design), product design (e.g., jewelry), and graphic/multimedia design.
If you want to create intricate and accurate freeform 3D modeling, with curves and organic forms, Rhino 3D is best at offering such flexibility. The software is constantly evolving to capture new, effective design features and tools. The latest version, “Rhino 8”, developed features for SubD modeling, ShrinkWrap, PushPull, Section Tools, and more to enhance design flexibility and performance.
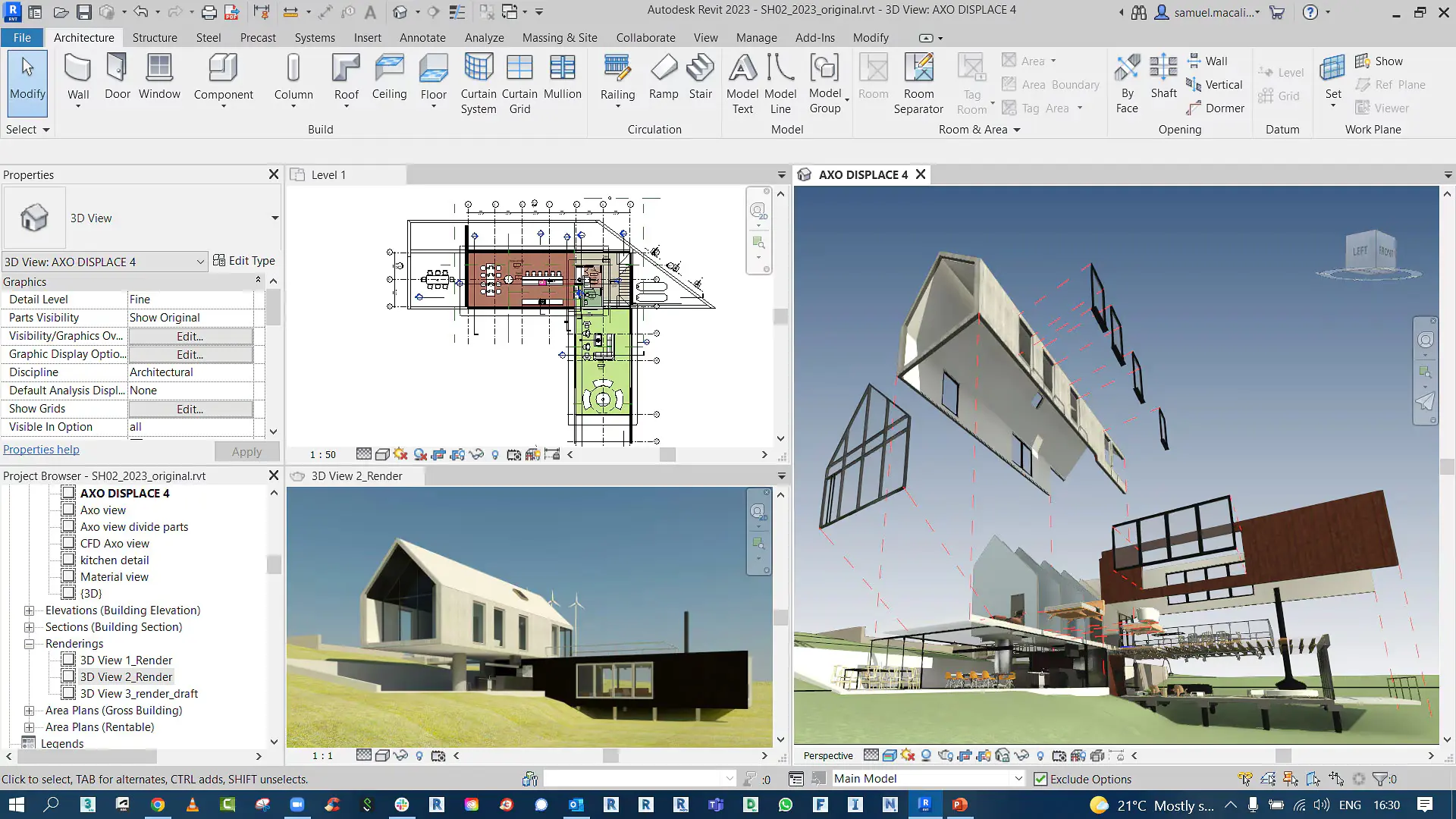
Revit is a BIM (Building Information Modeling) software initially developed by Charles River Software in 2000 and acquired by Autodesk in 2002. Its revolutionary features, such as parametric modeling, automation, collaboration tools, energy analysis, and construction documentation, make it a versatile tool for AEC professionals.
This software has positioned itself as a significant player in the BIM field, competing with tools like Archicad, Tekla Structures, and Bentley’s OpenBuildings Designer. If you want to create detailed architectural models that include structure, materials, and engineering-related aspects of buildings, Revit would be the go-to. Where accuracy and collaborative work are of the utmost importance, Revit streamlines project management capabilities for such complex building projects.
These software tools complement each other in helping professional designers across disciplines achieve conceptual and built design outcomes. Here’s a more detailed comparison of different technical aspects:
Revit → April 5, 2000
Rhino 3D → 1998
Revit → BIM software for architecture, engineering, and construction, focused on integrated building lifecycle management.
Rhino 3D → NURBS-based 3D modeling software used for architecture, industrial design, prototyping, engineering, product design, and more.
Revit → Building Information Modeling (BIM).
Rhino 3D → NURBS-based freeform 3D modeler with parametric, algorithmic, and generative design capabilities via Grasshopper3D.
Revit → Parametric 3D modeling where changes are automatically updated across the model; 2D documentation is extracted directly from the 3D model.
Rhino 3D → Precise NURBS geometry for complex curves and freeform surface modeling; parametric design through Grasshopper.
Revit → Best suited for standard architectural forms, MEP, and structural modeling; supports some complex geometries with adaptive components and Dynamo scripting.
Rhino 3D → Excels at highly complex, organic, and sculptural shapes with advanced surface modeling, computational design, and subdivision (SubD) tools.
Rhino 3D → 3DM (native), DWG, DXF, OBJ, STL, IGES, STEP, SAT, 3DS, FBX, PLY, WRL, CSV, AI, PDF, SVG.
Revit → RVT (native), DWG, DXF, DGN, SAT, SKP, STL, OBJ, FBX, NWC, NWD, IFC, GBXML.
Revit → Built-in multi-user collaboration with cloud-based workflows through Autodesk BIM Collaborate (formerly BIM 360), real-time co-authoring, and version control.
Rhino 3D → Primarily single-user; supports collaboration via plugins and external platforms like Rhino.Inside.Revit and cloud storage tools.
Revit → Extensive BIM-focused plugins and APIs; deep integration with Autodesk suite (Navisworks, AutoCAD, 3ds Max).
Rhino 3D → Wide plugin ecosystem, notably Grasshopper for parametric design, plus third-party tools for rendering, analysis, and interoperability.
Revit → Seamlessly integrates within the Autodesk ecosystem, plus VR/AR platforms and open standards like IFC.
Rhino 3D → Works with numerous CAD, CAM, rendering, and analysis tools; bridges to Revit through “Rhino.Inside” plugin; supports file exchange with many platforms.
Revit → Built-in energy and sustainability analysis; integration with Autodesk Insight and third-party performance analysis tools.
Rhino 3D → Geometry/surface analysis; sustainability and environmental analysis available via plugins (e.g., Ladybug Tools for environmental simulation).
Revit → Steep, due to BIM workflows, complex parametrics, and multidisciplinary coordination.
Rhino 3D → Moderate to steep, depending on the use of Grasshopper and advanced computational design features.
Revit → Built-in rendering with cloud rendering via Autodesk Rendering; advanced rendering possible via integration with 3ds Max and other tools.
Rhino 3D → Basic internal renderer; extensive support for high-end render engines like V-Ray, KeyShot, and Enscape via plugins.
Revit → Requires high-performance workstations with powerful CPUs and GPU.
Rhino 3D → Runs efficiently on moderate hardware; supports both Windows and macOS platforms.
Revit → Depending on the plan, subscription-based pricing ranges from $25 to $120/month.
Rhino 3D → Perpetual license model — €995 full, €595 upgrade, €195 for students/educators, €95 for academic upgrades.
You must be logged in to comment.