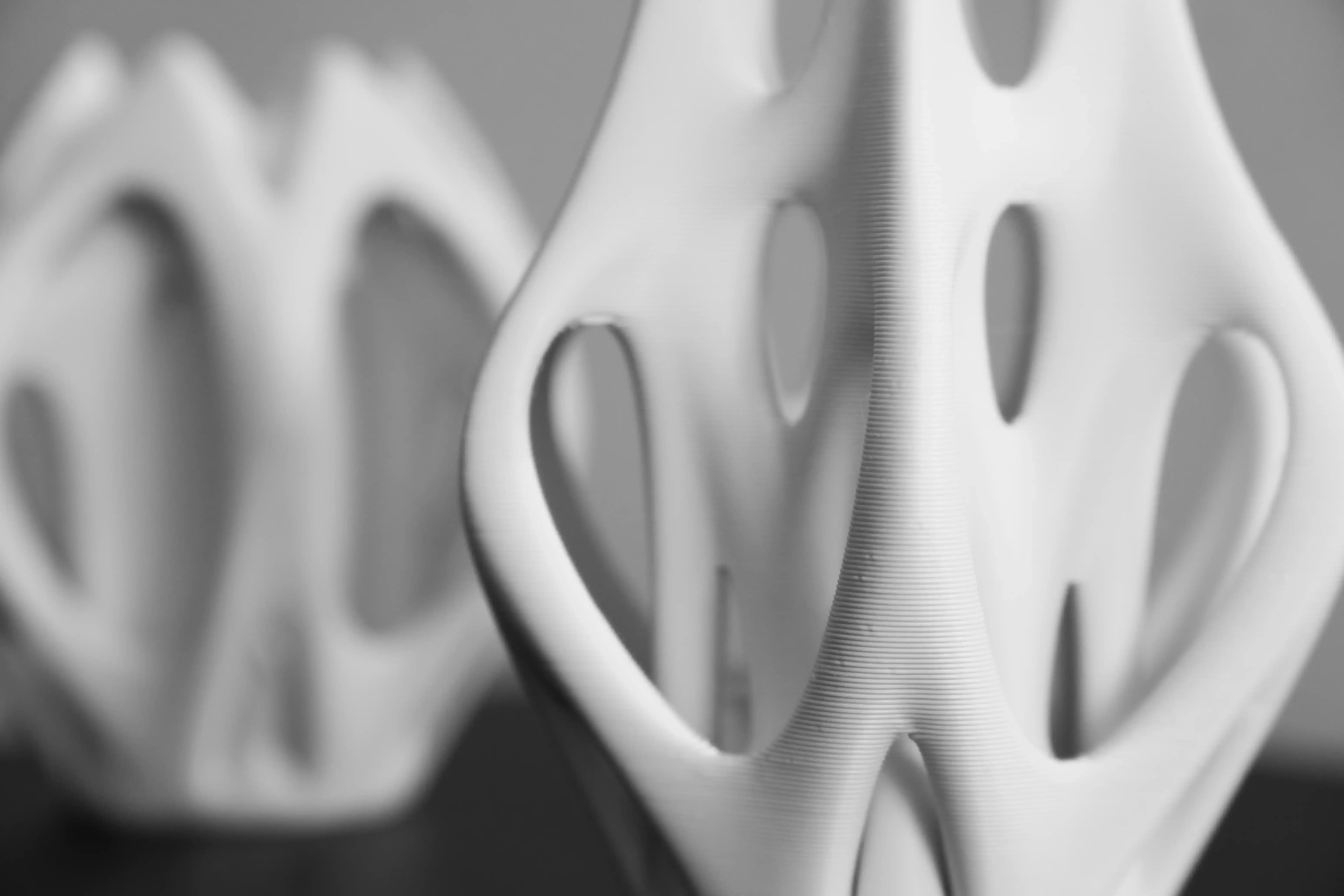

3D printing is affecting the architectural design industry by enabling professionals to turn digital concepts into tangible prototypes in a fast and precise manner, architects and designers use 3D printers for communicating design ideas and testing intricate architectural prototypes.
One commonly used 3D printing technology in architectural design prototyping is Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This 3D manufacturing process builds models layer by layer using thermoplastic filaments. Applying the FDM process is ideal for producing fast and affordable prototypes.
The FDM 3D printing workflow requires developing a 3D model from relevant 3D modeling tools, then converting the 3D design into an STL (stereolithography) or 3MF format, sending it to a slicer software, and finally converting the STL 3D model to a G-code that would run the process for the 3D printer.
As FDM 3D printing technology is increasingly integrated within architectural design workflows, choosing the right software tools is essential to ensure output accuracy and streamlined workflows for architects and designers. Below is a list of the best 3D modeling tools for that sense, as well as software that can connect such models' data to 3D printers, proposing a streamlined FDM 3D printing workflow for architects and designers to implement.
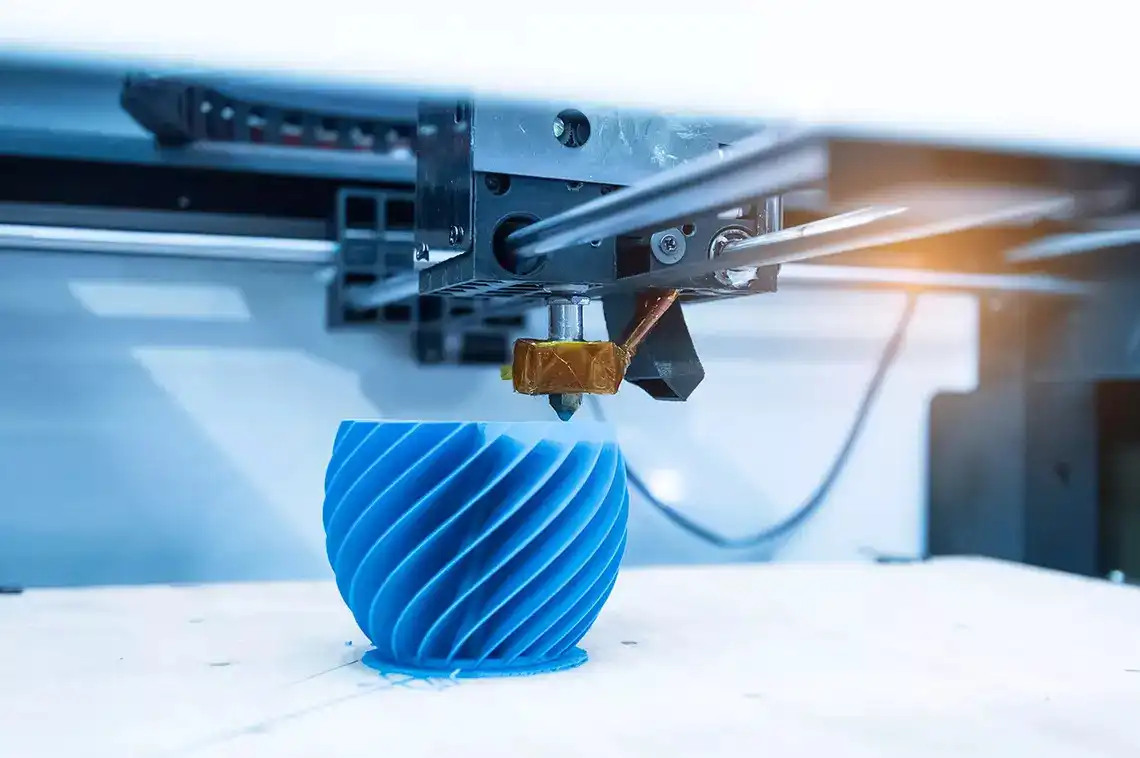

Several architectural modeling tools support STL export, enabling seamless transition to 3D printing. Here are the most commonly used programs:
Rhino3D stands out with its NURBS-based modeling features, alongside Grasshopper, which allows parametric and complex geometric modeling for architects and designers, both can produce precision-based flexible models.
Rhino3D supports STL export with control over mesh detail, and it is ideal for producing complex models ready for 3D printing.
SketchUp is popular for its straightforward and fast 3D modeling processes for architects and designers.
With the help of STL export extensions within SketchUp, architects can prepare such models for 3D printing. It would be ideal to implement SketchUp for the conceptual and massing stages of the design process.
Although Fusion is more common in mechanical and industrial fields, it would be beneficial for architects and designers who are dealing with producing detailed components, furniture design, or custom 3D geometry.
Fusion can export models in STL format, meaning that it can be used as part of a 3D printing workflow.
Blender is an open-source 3D modeling software that is used within various industries, including architecture.
Blender offers a unique tool feature “3D Print Toolbox”, allowing to analyze the 3D models and identify if the models would need adjustments, such as checking if the model is fully connected as a whole, or the model is thick enough for printing, which are essential for achieving accuracy in the printing process.
These tool features help to optimize the 3D printing stage of the design when using Blender.
Revit is mainly a BIM (Building Information Modeling) software for developing highly detailed building models. Revit can export models to STL format.
There might be some refinement processes needed when exporting the 3D model, but overall, it is a strong option for developing 3D printing workflows of BIM-based models.
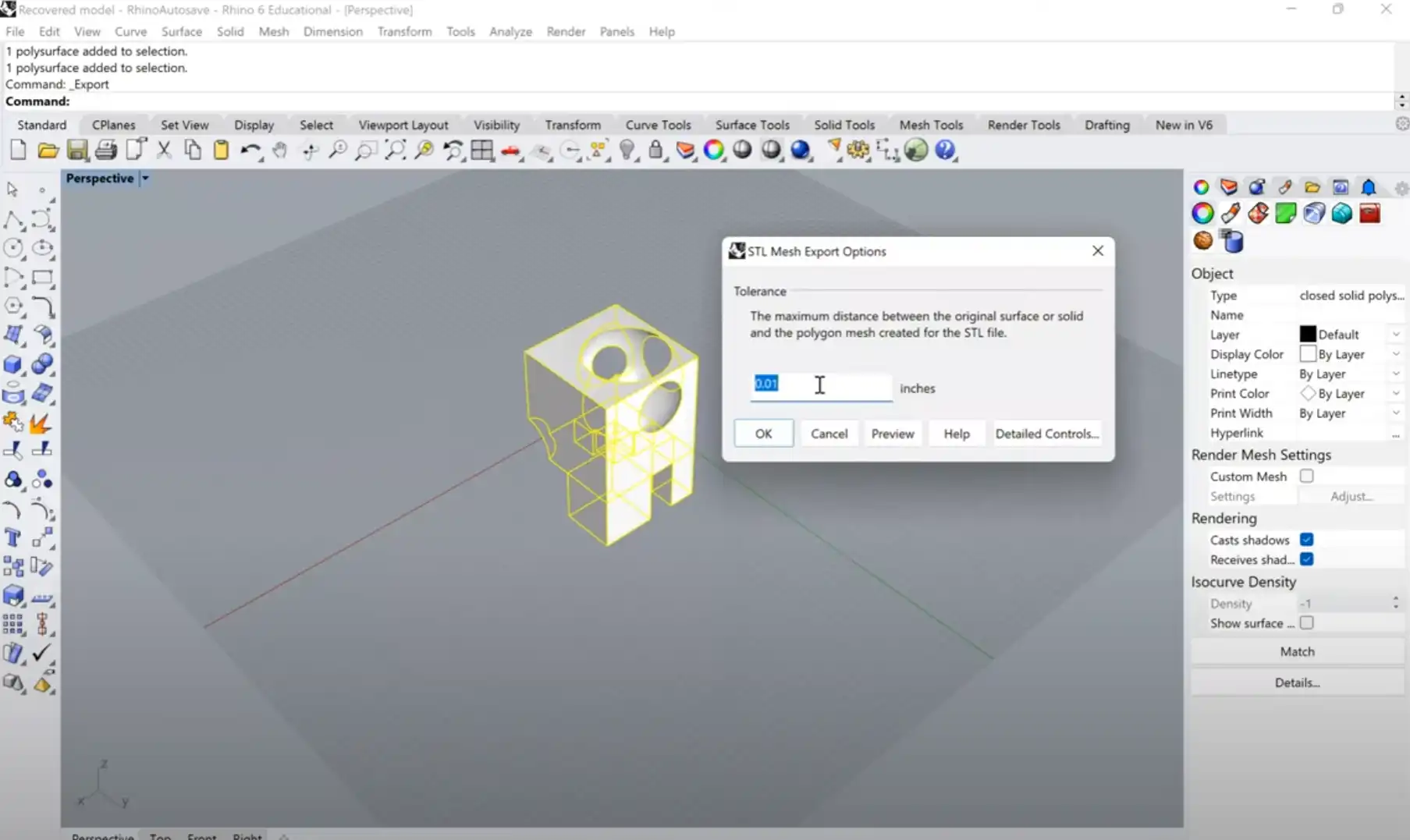
Once a 3D model is exported as STL or 3MF format, the next step is to import the 3D model file into a slicer software that performs the process of 3D printing.
These tools, known as slicers and printer interfaces, handle everything from converting architects and designers' 3D models into printer-readable instructions (G-code) to managing the print process itself.
Cura is a commonly used slicing software that translates STL, OBJ, and 3MF files into G-code for 3D printers. It provides a user-friendly interface and robust print options, allowing architects and designers to access easy and precise printing processes.
In that sense, Cura is highly compatible with the 3D modeling tools relevant to the architectural field, as all these tools depend on exporting an STL format of the models.
Check out the PAACADEMY course, “3D-Printing Innovations with FDM” which explores turning digital designs into physical objects, empowering architects and designers with the necessary skills to implement such 3D printing workflows.
PrusaSlicer supports STL, OBJ, and 3MF files, ensuring seamless compatibility with Rhino3D, SketchUp, Fusion 360, Blender, and Revit.
Whether exporting from Rhino or other 3D modelling tools, PrusaSlicer helps ensure reliable prints with its customizable details and tool features available.
Developed by Bamby Lab, Bambu Studio is a high-performance slicer software, designed specifically for their high-speed 3D printers. It supports an easy-to-use interface and has the ability to import STL-based 3D models.
Bambu Studio has its options primarily optimized for Bambu Lab printers, in that sense, users might experience some limitations and reduced functionalities if using a non-Bambu 3D printer.
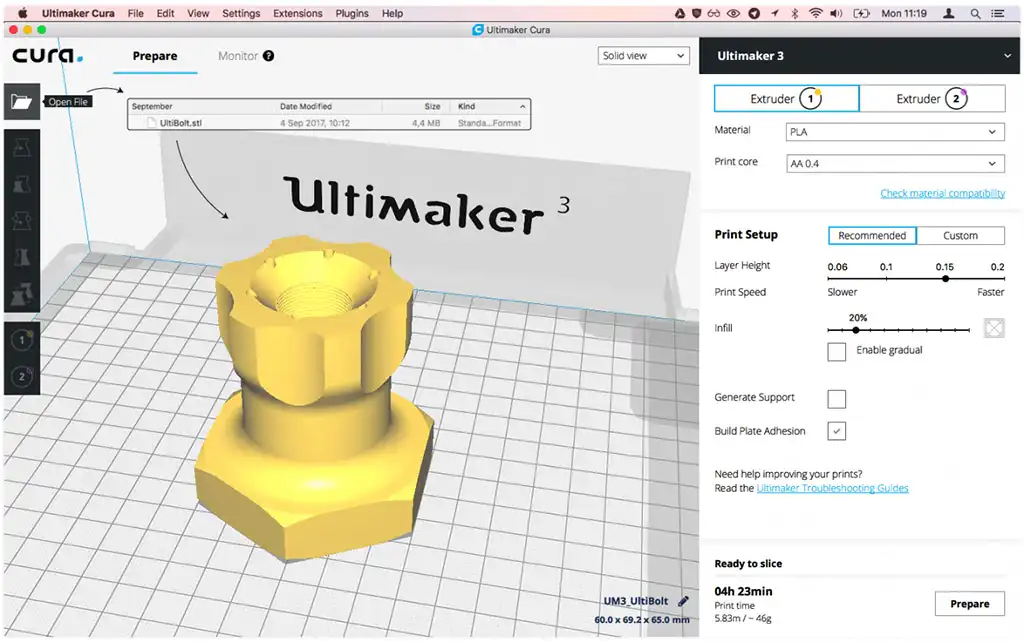
The rise of 3D printing in the architectural design practice has led to new digital workflows where design and fabrication have the potential to be connected within a harmonious design process.
Integrating advanced 3D modeling tools such as Rhino3D, SketchUp, Fusion 360, Blender, and Revit, with slicing software like Cura, PrusaSlicer, or Bambu Studio, streamlines the FDM 3D printing workflow, allowing architects and designers to move seamlessly from digital design to physical prototypes with greater precision.
You must be logged in to comment.